United States military weapons
Small Arms The basics of basics are the small arms weapons used by the individual infantryman. Here are the basic small arms used by the United States Army:  M16A2 Rifle. The M16A2 is the standard issue rifle. It's carried by pretty much every soldier in a combat zone. Most people simply call it the M-16. The M-16 has been around in one version or another since the Vietnam war (the first version, the M16A1 entered Army service in 1964). It's longevity is creditable to its usefulness as a general assault weapon. It's quite simply one of the finest military rifles ever made (although advocates of the M-4 Carbine may argue with me). The rifle is lightweight, simple to operate, and puts out a lot of lead. M16A2 Rifle. The M16A2 is the standard issue rifle. It's carried by pretty much every soldier in a combat zone. Most people simply call it the M-16. The M-16 has been around in one version or another since the Vietnam war (the first version, the M16A1 entered Army service in 1964). It's longevity is creditable to its usefulness as a general assault weapon. It's quite simply one of the finest military rifles ever made (although advocates of the M-4 Carbine may argue with me). The rifle is lightweight, simple to operate, and puts out a lot of lead.The M16A2 5.56mm rifle is a lightweight, air-cooled, gas-operated, magazine-fed, shoulder or hip-fired weapon designed for either automatic fire (3-round bursts) or semiautomatic fire (single shot) through the use of a selector lever. The weapon has a fully adjustable rear sight. The bottom of the trigger guard opens to provide access to the trigger while wearing winter mittens. The upper receiver/barrel assembly has a fully adjustable rear sight and a compensator which helps keep the muzzle down during firing. The steel bolt group and barrel extension are designed with locking lugs which lock the bolt group to the barrel extension allowing the rifle to have a lightweight aluminum receiver. Primary function: Infantry weapon Manufacturer: Colt Manufacturing and Fabrique Nationale Manufacturing Inc. Length: 39.63 inches (100.66 centimeters) Weight, with 30 round magazine: 8.79 pounds (3.99 kilograms) Bore diameter: 5.56mm (.233 inches) Maximum effective range: Area target: 2,624.8 feet (800 meters) Point target: 1,804.5 feet (550 meters) Muzzle velocity: 2,800 feet (853 meters) per second Rate of fire: Cyclic: 800 rounds per minute Sustained: 12-15 rounds per minute Semiautomatic: 45 rounds per minute Burst: 90 rounds per minute Magazine capacity: 30 rounds Unit Replacement Cost: $586 M-4 Carbine The M-4 combat assault rifle first entered Army service in 1997. The rifle is the standard weapon used by some Army units such as the 82nd Airborne Division and special operations units, such as Army Rangers.  With a shortened barrel and collapsible stock, the M-4 is ideal for close quarter marksmanship where light weight and quick action are required. Firing a standard 5.56 millimeter round, the weapon weighs a mere 5.6 lbs. (empty). A revised rear sight allows for better control of the weapon out to the maximum range of the ammunition used. With the PAQ-4 (Infrared Sight) mounted on the forward rail system, the M-4 can be fitted for increased firepower. With a shortened barrel and collapsible stock, the M-4 is ideal for close quarter marksmanship where light weight and quick action are required. Firing a standard 5.56 millimeter round, the weapon weighs a mere 5.6 lbs. (empty). A revised rear sight allows for better control of the weapon out to the maximum range of the ammunition used. With the PAQ-4 (Infrared Sight) mounted on the forward rail system, the M-4 can be fitted for increased firepower.The M-4 Carbine can also be fitted with the M-203 40mm grenade launcher. The M-203 is a lightweight, compact, breech loading, pump action, single shot launcher. The launcher consists of a hand guard and sight assembly with an adjustable metallic folding, short-range blade sight assembly, and an aluminum receiver assembly which houses the barrel latch, barrel stop and firing mechanism. The launcher is capable of firing a variety of low velocity 40mm ammunition. The launcher also has a quadrant sight that may be attached to the M-4 carrying handle and is used when precision is required out to the maximum effective range of the weapon. The M-4 in this photograph also has an M-68 close-quarters battle sight mounted on the rear rail and a PAQ-4 infra-red sight on the forward rail. Type: Compact assault rifle Entered Army Service: 1997 Specifications: Caliber: 5.56mm Weight: 5.65 lbs Range: 500 m Rate of fire: variable, depending on rate selected M-24 Sniper Weapon  The M24 Sniper's Weapon System (SWS) represents a return to bolt action sniper rifles by the US Army. The rifle entered Army service in 1998. The M24 uses the Remington 700 action, although the receiver has been made for adaptation to take the .300 Winchester Magnum round. The stock (HS Precision) is made of a composite of Kevlar, graphite and fiberglass bound together with epoxy resins, and features aluminum bedding block and adjustable butt plate. A detachable bipod (Harris) can be attached to the stock's fore-end. The M24 Sniper's Weapon System (SWS) represents a return to bolt action sniper rifles by the US Army. The rifle entered Army service in 1998. The M24 uses the Remington 700 action, although the receiver has been made for adaptation to take the .300 Winchester Magnum round. The stock (HS Precision) is made of a composite of Kevlar, graphite and fiberglass bound together with epoxy resins, and features aluminum bedding block and adjustable butt plate. A detachable bipod (Harris) can be attached to the stock's fore-end.The rifle is a bolt-action, six-shot repeating rifle (one round in the chamber and five rounds in the magazine). It is used with either the M3A telescope (day optic sight, usually called the M3A scope, a 10X fixed Leupold M3 Ultra telescope) or the metallic iron sight. This is the sniper weapon used by the Army. Caliber: 7.62x51mm NATO (.308 win) Operation: Bolt Action Feed: 5-Round internal magazine Weight: 12.1 lb (5.49 kg) empty without telescope Length: 43in (1092mm) Sights: 10x42 Leupold Ultra M3A telescope sight (Mil-Dots), plus detachable emergency iron sights. (Redfield Palma International) Barrel: 24" length, 1 twist in 11.2", 5 lands & grooves. Stock: HS Precision - adjustable length. Max Effective Range: 800 meters (875 yards) Expected Accuracy: 1 MOA with M118 (Ammo is limiting factor) M40A1 Sniper Rifle  This is the preferred sniper rifle for the U.S. Marine Corps. The M40A1 sniper rifle is based on the Remington model 700. It is a heavy barrel, bolt action, magazine fed 7.62mm rifle that is optimized for accuracy with Match Grade ammunition. The rifle is equipped with a special 10 power Unertl sniper scope. With scope, the rifle weighs approximately 14.5 pounds. It is equipped with a built-in five round magazine. This is the preferred sniper rifle for the U.S. Marine Corps. The M40A1 sniper rifle is based on the Remington model 700. It is a heavy barrel, bolt action, magazine fed 7.62mm rifle that is optimized for accuracy with Match Grade ammunition. The rifle is equipped with a special 10 power Unertl sniper scope. With scope, the rifle weighs approximately 14.5 pounds. It is equipped with a built-in five round magazine.The unique characteristics of the M40A1 Sniper Rifle are: commercial competition-grade heavy barrel, McMillan fiberglass stock and butt pad, modified Winchester Model 70 floor plate and trigger guard, and modified and lightened trigger. In addition, each stock is epoxy bedded for accuracy and all weapons must shoot less than one minute of angle (MOA). The M40A1 was put into service in the 1970s to meet the need of a long range sniper rifle. Each rifle is hand built by specially trained and qualified personnel at the Marine Corps Marksmanship Training Unit (MTU) at Quantico, Virginia. Length: 44 inches (111.76 centimeters) Barrel length: 24 inches (61 centimeters) Weight: 14.5 pounds (6.58 kilograms) Bore diameter: 7.62mm (.308 inches) Maximum effective range: 1000 yards (914 meters) Muzzle velocity: 2550 feet (777 meters) per second Chamber pressure: 50,000 psi Magazine capacity: 5 rounds Unit Replacement Cost: $2,105 M-249 SAW  The M-249 is unofficially called the Minimi. The official name for the weapon is SAW which means Squad Automatic Weapon. Early test versions of the M-249 were plagued with problems, but the current model is considered reliable. The weapon entered Army service in 1987, replacing the M-60 Machine Gun. The M-249 is unofficially called the Minimi. The official name for the weapon is SAW which means Squad Automatic Weapon. Early test versions of the M-249 were plagued with problems, but the current model is considered reliable. The weapon entered Army service in 1987, replacing the M-60 Machine Gun.The M-249 is a .223 cal (5.56mm) gas operated light weight machine gun which feeds from a belt held in a 100 or 200 rounds box under the gun. This weapon has a plastic pistol grip and a folding stock so it can be kept compact and light. The M-249 machine gun is an ideal complementary weapon system for the infantry squad platoon. It is light enough to be carried and operated by one man, and can be fired from the hip in an assault, even when loaded with a 200-round ammunition box. The barrel change facility ensures that it can continue to fire for long periods. The US Army has conducted strenuous trials on the M249, showing that this weapon has a reliability factor that is well above that of most other small arms weapon systems. The weapon is used by the U.S. Army and the U.S. Marine Corps. Type: Squad automatic weapon Entered service: 1987 Specifications: Caliber: 5.56mm Length:100 cm Weight:16.3 lbs Range: 800 meters Rate of fire: 750 rounds per minute M-240 Machine Gun  The M-240 entered Army and Marine Corps service in 1997. The M-240 is a version of FN's MAG 58 general-purpose machine gun. The M-240 fires the 7.62mm NATO round and is very reliable, with an estimated 26,000 Mean Rounds Between Failure (MRBF). The M-240 entered Army and Marine Corps service in 1997. The M-240 is a version of FN's MAG 58 general-purpose machine gun. The M-240 fires the 7.62mm NATO round and is very reliable, with an estimated 26,000 Mean Rounds Between Failure (MRBF).Advantages of this weapon include its popularity with other nation's forces and number of configurations. For example, in a helicopter crash, the M-240d helicopter-mount version could be quickly modified by installing the bipod and butt stock of the M-240b version, which would then allow the weapon to be used for self defense by the surviving helicopter crew members. The M-240 is manufactured in the following configurations: M-240b is designed for infantry use. The "B" version weapon is equipped with a thermal shield over the rear of the barrel to protect the operator. The M-240c version is designed for use internally in M2/M3 Bradley Infantry Fighting Vehicle. The M-240d is designed for use on pintel mounts in helicopters and on the outside of tanks and armored vehicles. The M-240g version is used by special operations forces. The heat shield on this version is removed and there are special fittings for night sights. Type: Medium machine gun Entered service: 1997 Specifications: Caliber: 7.62mm Weight: 27.6 lbs Range: 1,100 m Rate of fire: 600-9 rounds per minute |
Mk.19 (Mark 19) automatic grenade launcher
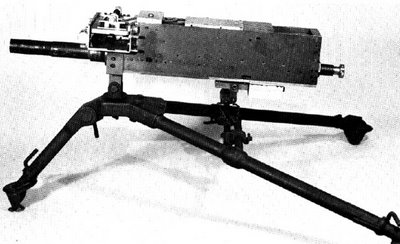




Caliber: 40x53mm High Velocity
Type: blowback operated, belt fed automatic grenade launcher
Overall length: 1095 mm
Weight: 35.3 kg gun body plus 20 kg M3 tripod mount or 9.1 kg lightweight tripod mount
Effective range: up to 1500 m (point target); 2200 m maximum range
Rate of fire: 300 - 400 rounds per minute
Development of the Mark 19 (Mk.19 in short) grenade machine gun was initiated by US Navy in 1966, after the initial experience gained during Vietnam war. Since about 1962, US forces in Vietnam used several multi-shot 40mm grenade launchers that fired low velocity 40x46mm M406 grenades originally developed for M79 single-shot weapon. Among these, most notable was the Mark 18 belt-fed grenade launcher, developed by Hughes corporation; this was a hand-cranked weapon that provided significant short-range firepower to riverine crafts and marine infantry. However, all such weapons lacked effective range, and US Navy decided to develop a new, automatic, self-powered weapon around the high-velocity 40x53mm M384 grenade (which was originally developed for US Army's M75 automatic grenade launcher, used on UH-1 and AH-1 combat helicopters). Development of Mark 19 automatic grenade launcher began in July 1966, and by October 1967 firs three working prototypes of the new weapon were ready for official field trials. The production Mark 19 Model 0 grenade launchers entered service in Vietnam in early 1968, on board of riverine crafts and UH-1 Huey gunship helicopters belonging to US Navy. In around 1971, the basic design was slightly improved, and type classified as Mark 19 Model 1; these weapons were manufactured by US Naval Ordnance Station Louisville. In around 1974, US Navy attempted to produce more streamlined version of the basic design, known as Mk.19 Mod.2, but this development never went past prototype stage, and in 1976 work began on simplified and more robust improved version of the Mk.19, which was type classified as Mark 19 Model 3 (Mk.19 mod.3) in 1981. The manufacturing contract for Mk.19 Mod.3 weapons was granted to Saco Defence (now General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products - GDATP). By the year 2000, at least 25 thousands of Mk.19 mod.3 grenade launchers were in service worldwide, mostly with all branches of US armed forces.
The Mark 19 Model 3 (Mk.19 mod.3) automatic grenade launcher is air cooled, belt fed, blowback operated machine gun. It fires from open bolt and uses advanced primer ignition principle to decrease peak recoil. To provide minimum of parts and maximum reliability of feeding, Mk.19 uses two-stage feed, when each round is first withdrawn rearwards from the belt on the opening stroke of the belt and then placed into T-slot cut in the bolt face; on the closing stroke, the round is already properly positioned on the bolt and is feed straight to the chamber; empty cartridge cases are ejected to the bottom as they are pushed down from the T-slot by the next cartridge (the same principle has been employed on some WW1 era machine guns). Ammunition is fed using special disintegrating belt; when rounds are fed into the chamber, links stay on the case and are ejected from the gun along with spent cartridge cases. Ammunition is usually supplied in belt boxes with capacity of 32 or 48 rounds. Loaded 32-round box weights about 19 kg (42 lbs). Mk.19 grenade launcher is fitted with dual spade grips, and can be fired in semi-automatic of full automatic modes. Alternatively, electric trigger pack can be installed for remote controlled mounts. It can be installed on standard M3 tripods (using Mark 64 cradle / adapter) for infantry use, or on various vehicle mounts on jeeps, armored vehicles, naval vessels etc. By default, Mk.19 mod.3 grenade launchers are equipped with machinegun type iron sights, but other types of sighting equipment (including night sights and range-finding electronic sights) are available. Today the primary ammunition type for Mk.19 mod.3 in US service is the 40mm M430 High Explosive, Dual Purpose (HEDP) round, which can penetrate up to 50mm (2") of rolled homogenous armor and provide effective anti-personnel fragmentation effect with damage radius of about 15 meters (lethal damage / kill zone radius 5 meters).




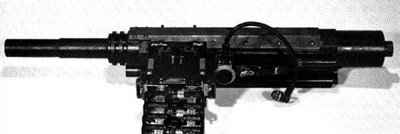
Caliber: 40x53mm High Velocity
Type: short recoil operated, belt fed automatic grenade launcher
Overall length: 940 mm
Weight: 18 kg gun body; 41 kg complete with Mk.108 tripod and AN/PWG-1 video sight
Effective range: up to 1700 meters against point targets, up to 2200 m maximum
Rate of fire: 225-300 rounds per minute
The development of the more lightweight and effective weapon which could replace venerable Mk.19 Mod.3 automatic grenade launcher in US and foreign service, has been initiated by Saco Defense Company (now General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products - GDATP) during late 1980s.First prototypes of the new weapon appeared by mid-1990s, and in 1995 US DoD approved the industry team which then consisted of Saco Defense (now GDATP) as a weapon producer and system integrator, and Raytheon as a provider of advanced electronic sighting and fire control equipment. Later on, team was joined by Norwegian NAMMO Oy company, which develops the advanced, air- bursting 40mm ammunition for new weapon. In the year of 2003, US Special Operation Command (USSOCOM) adopted the GDATP Striker 40 40mm automatic grenade launcher as Mark 47 model 0, complete with its new tripod mount and AN/PVG-1 Lightweight Video Sight developed by Raytheon. These weapons now (February 2006) are in limited service with US Special Operation forces in Afghanistan and Iraq, and also are being considered for adoption by US Marine Corps. Mk.47 grenade launchers are compatible with full spectrum on NATO-standard 40mm high velocity ammunition; advanced air-bursting ammunition with programmable fuses is being developed for this weapon. Once this ammunition will be available, the Mk.47 / Striker 40 weapon system will provide serious and more cost-effective alternative to the much-discussed 25mm XM307 ACSW weapons now in development.
Mark 47 Model 0 (mk.47 mod.0) automatic grenade launcher is short recoil operated, locked breech weapon that fires from closed bolt for improved first-shot hit probability. Weapon is air-cooled and belt fed, using standard disintegrating belts, same as Mk.19 Mod.3 launcher. Standard belts are supplied in 32 or 48 round boxes. Weapon is equipped with newly developed Mk.108 mod.0 tripod with T&E mechanisms and brake that allows to lock weapon on pre-selected target spot. The key member of the Striker 40 system is the AN/PVG-1 Lightweight Video Sight (LVS), which offers 3X magnification TV view on target, combined with laser range finder and ballistic computer; sight also has interface connectors that allow to link it to optional thermal night sighting equipment which can be installed on the weapon; once the night sight is connected, operator can select TV or thermal picture via the single button. The LVS allows to accurately measure the range to the target then aim the gun accurately for high first shot hit accuracy. LVS is installed on the right side of the weapon, and is controlled by the buttons and four-position "joystick" located at the rear of the receiver, between and above spade grips.
XM307 ACSW Advanced Crew-Served Weapon



Caliber: 25x59mm
Type: gas operated, belt fed automatic grenade launcher
Overall length: 1328 mm
Weight: 22.7 kg complete with tripod mount and sight / fire control unit
Effective range: up to 2000 m against point targets, 3600 m maximum
Rate of fire: 250 rounds per minute
The origins of the XM307 Advanced Crew Served Weapon (ACSW), also known as XM307 25mm Airbursting Weapon System, lie in the several military documents, published in USA during late 1980s. These documents stated that current small arms have reached its peak in development, and the only currently possible way to increase combat effectiveness and single-shot lethality of such weapons is do develop new guns that will fire air-bursting munitions with programmable fuses. Following these conclusions, US Army initiated development of several so-called Objective weapons; two most famous of these were XM29 Objective Individual Combat Weapon (OICW) and XM307 Objective Crew-Served Weapon (OCSW), currently renamed to Advanced Crew-Served Weapon (ACSW). After much development, the prime contractor for ACSW program was selected as General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products (GDATP). The development team for ACSW also includes General Dynamics Ordnance and Tactical Systems (air-bursting ammunition), Kaman Dayron Inc (programmable fuze) and Raytheon (computerized fire control system). First demonstrated in around 1999 as 25mm OCSW, at the present time (early 2006) the XM307 ACSW is on advanced stages of development, with several prototypes already tested with live ammunition, including air-bursting rounds. Initial plans called for first US Army units to be equipped with 25mm M307 ACSW weapons by 2008; M307 shall replace in service the older weapons like Mk.19 Mod.3 40mm grenade launchers and .50 caliber M2HB machine guns. For added versatility, XM307 can be easily converted to fire .50 caliber machinegun ammunition (12.7x99) with replacement of just 5 parts.
The key to greatly increased combat effectiveness of ACSW system is programmable air-bursting ammunition, which will be used in conjunction with electronic fire control unit. This ammunition will allow to precisely engage enemy personnel in open or in defilade, without the need for direct impact in the target area. Other types of ammunition proposed for XM307 ACSW are HEAT (with required armor penetration up to 5cm / 2in), less-lethal (with tear gas for peace-keeping applications) and training rounds with dummy warheads.It is obvious that by the year 2008 the XM307 will enter into strong competition with several 40mm air-bursting weapons such as Mk.47 Striker 40, and the outcome of this competition is hardly predictable, as either system has its own merits and downsizes. ACSW is certainly lighter, fires lighter ammunition (allowing to carry more ammo in the same weight), and has longer range. 40mm weapons fire bigger warheads and can use huge stocks of already existing and well developed NATO-standard ammunition of various types, including point-detonating FRAG, HEDP, AP, less-lethal and many others.
XM307 Advanced Crew Served Weapon is gas operated, rotating bolt locked weapon that uses differential recoil system for decreased peak recoil. XM307 is belt fed weapon that fires from open bolt. The differential recoil system means that barrel and bolt group are allowed to recoil within the receiver casing together, against the recoil springs. When weapon is cocked for first shot, bolt is locked open and the entire barrel/bolt group is carried rearwards and also locked there. Upon the pull of the trigger both barrel group and the bolt inside it are released, and the bolt loads the round and locks it in chamber while barrel still moves forward; firing pin is then released immediately, and the recoil from the discharge first has to arrest the forward movement of the barrel group, and then throws it backward with less force than it would in the traditional system with fixed barrel. The belt feed and bolt cycling are operated by conventional gas action. The fire control unit includes zoomable day and night vision channels that output the sight picture to the small display at the rear of the sight. Integral laser range-finder allows for precise range measurement, necessary for automatic point of aim correction and for programming of the air-bursting fuzes. XM307 weapon is fitted with dual, ergonomically shaped spade grips with triggers and fire and sight control buttons. Additional buttons are located at the rear of the sight / fire control unit, below the eyepiece. In standard applications, XM307 can be used either on lightweight infantry tripod, or on vehicle mounts, manually or remotely controlled. For vehicular applications, GDATP will develop the dual feed option, which will allow to select the type of ammunition (anti-personnel HEAB or armour-piercing) at the instant before firing.





The Glock family of pistols, once started by famous Glock 17 pistol, was developed by Austrian company Glock Gmbh., previously known for quality knives and entrenching tools. The Glock 17 pistol first appeared at the Austrian Army trials, won it and was adopted by Austrai Army and Police in the early 1980s under the designation of P-80. Since then, the Glock 17 and its descentants become very popular military and law enforcement firearms, being exported in more than 50 countries. Currently, Glocks are chambered in all major pistol calibers, namely 9x17mm Short (.380ACP), 9x19mm Luger, .357SIG, .40SW, 10mm auto and .45ACP. Also, Glocks available in full-size service models, semi-compact models, compact models for concealed/backup carry, and in longslide competition models. Training versions, firing non-lethal practice ammo, also available. Training versions are distinguished from "live" ones by frame colour - blue frame for guns that fire non-lethal ammunition and red frame - for non-firing guns.
All Glocks (except for ones chambered in 9x17 - .380ACP) are recoil operated, locked breech pistols. Glocks feature Browning-type linkless locking system with barrel interlocking with slide via ejection port. All Glocks feature patented "Safe action" striker-fired trigger mechanism. After the each cycle of the slide the striker is set to half-cock position and is safely blocked by internal safety. When shooter pulls the trigger, he disengades the trigger safety first, then cocks the striker to the full-cock and then fires the gun. This results in constant trigger pull (ajustable from 2 to 5.5 kg) and, unlike the traditional DA or DAO pistols, unavailability of the "second strike" option in case of the misfire. All Glocks has no external controls except the trigger and the slide stop (the only different is Glock 18, which has slide mounted fire mode selector).
The .380ACP / 9x17mm Short chambered Glocks (models 25 and 28) differs from the rest of the Glock family by operating by simple blowback principle. These pistols targeted for civilian markets where ownership of the firearms chambered in "military" calibers is prohibited, or for those shooters who can't withstand more severe recoil of the "bigger" calibers.
All Glocks feature polymer frame, steel slides made by precision moulding process and had Tenifer heat-threatment to increase rust and wear risistance. early Glocks had plain grips with slight serrations. Modern variants has finger grooves on the front strap of the grip, and ambidextrous thumb rests. Also, modern versions featured underbarrel acessory rails. Barrels has hexagonal rifling in all calibers. Both front and rear sights are dovetailed and usually had white or luminous inserts. Ajustable sights are available for competition models.
Almost all models had modifications with factory-ported barrels. These models are marked with suffix "C" after the model number, i.e. Glock 17C.
The Glock 17 (and only model 17) could be modified with "amphibious kit" that allows underwater firing (in wery shallow depths, thought). Basically, the underwater shooting itself has wery little effect in real combat, since the effective range is extermely short. The real purpose of that feature is to show the strenght of the gun and to allow safe shoting in severe weather conditions, with possible water in the barrel (in many guns this may result in blown barrel).
The select-fire version of the Glock, called Glock 18, available only in 9mm Luger and only for Military / Law enforcement sales. Glock 18 could fire single shots or three-shot bursts. Glock 18 may be equipped with 31-rounds extended magazines and after-market folding stocks. For security reasons, some parts of the Glock 18 ARE NOT interchangeable with Glock 17/19 pistols. The theoretical rate of fire in full-auto mode is 1200 rounds per minute.
Steyr GB (Austria)


Type: Double Action
Chamber: 9x19mm Luger/Parabellum
Weight: 845 g empty; 1285 g loaed
Length: 216 mm
Barrel length: 136 mm
Capacity: 18 rounds
The development of the GB pistol was started by Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG (now Steyr-Mannliher AG), Austria, in the early 1970s, when the Austrian army announced its plans to replace aging P38s and High Powers with the new pistol. Original design, labelled as PI-18, was developed in 1974, and final version, called GB, entered production in 1981. The production of the GB was ceased circa 1988, after some 15.000 to 20.000 pistols had been produced.
The GB is a blowback-operated, gas-retarded blowback semi auto pistol. It uses some of the hot powder gases, feed from the barrel into the front part of the slide, to slow down the retraction of the slide before the bullet leave the barrel. This scheme was developed by German engineer Barnitzke at the end of the WW2. The gas brake is formed by the barrel, its bushing and the slide.The trigger of the GB is of double action design, with the slide mounted decocker lever. GB also featured firing pin block that unlocks the firing pin only when the trigger is completely depressed.
The frame and the slide is made from carbon steel with special high-strenght finish. Barrel has polygonal rifling and is chrome lined, and solidly attached to the frame.The sights are fixed and featured white-dot inserts (one in the front sight blade and two - around the rear sights notch). Some early GBs were manufactured with steel grip panels, with all the rest manufactured with plastic checkered grips.
Thanks to its gas-retarded blowback design and solid weight, that resulted in low felt recoil, and to the barrel with polygonal rifling, that toesn't move when firing, the Steyr GB displayed wery good accuracy. The reliability is also adequate, at least. While the GB failed at the Austrian and USA Army pistol trials (won respectively by Glock 17 and Beretta 92FS-B), it was used by some Law Enforcement and Special Operations forces, and also was sold to civilians in Europe and USA.
Ballester-Molina / Ballester-Rigaud pistol (Argentine


Type: Single Action
Calibers: .45ACP
Weight unloaded: 1075 gram
Length: 216 mm
Barrel length: 127 mm (5")
Capacity: 7 rounds
The Ballester-Molina pistol, originally known as Ballester-Rigaud (so marked during first years of manufacture, circa 1938 to 1940), were made in Argentine by Hispano Argentina de Automotives SA (HAFDASA) company. Manufacture started in 1938 in attempt to provide Argentinean police and military with less expensive alternative to the Colt modelo 1927 pistol, domestically made licensed copy of the American Colt M1911A1 pistol. Production of the Ballester-Molina ceased in the early 1950s. While Ballester-Molina pistol is externally very similar to Colt, it has significant differences, especially in the safety and trigger unit arrangements. Actually, the only parts exchangeable between Ballester-Molina and M1911A1 are the barrel with link and the magazine. The trigger and safety arrangements were more or less copied from the Spanish Star pistols, with the pivoting trigger, single trigger to sear link, and no grip safety. Ballester-Molina pistols were used by Argentinean military and police, as well as supplied to the Britain during Second World war. Britain issued these pistols to their Special Operations Executives agents, which usually operated behind enemy lines.
The Ballester-Molina pistol is a short recoil operated, locked breech pistol. the locking system is similar to that of Colt M1911A1, with the swinging link used to unlock the barrel from the slide. The single action trigger is pivoted on the axis, the frame-mounted manual safety locks the slide and the hammer
Bersa Thunder-380 pistol (Argentine)


Type: Double Action
Calibers: 9x17mm Short/Kurz (.380ACP) and 7.65x17SR (.32ACP)
Weight unloaded: 560 gram
Length: 168 mm
Barrel length: 90 mm
Capacity: 7 (9mm) or 9 (7.65mm) rounds standard
Bersa Thunder-380 pistols are manufactured in Argentine by Bersa S.A. company, as a compact self-defense side arms for civilians and police. being inexpensive and of good quality, these pistols offer a good level of protection with decent ergonomics. These pistols must not be confused with larger and more powerful Bersa Thunder 9 and Thunder 40 pistols from the same company.
Bersa Thunder-380 pistols are simple blowback operated, with the return spring located around the barrel. The trigger is of double action type, with exposed hammer. The safety switch is located at the left side of the frame, and, when engaged, automatically decocks the hammer. There is also an internal firing pin safety, which blocks the firing pin unless the trigger is pressed. Magazine release button is located above and behind of the trigger guard, at the left side of the frame, and just below of the slide stop lever. Single stack magazine holds seven 9mm (.380) or nine 7.65mm (.32) rounds. Deluxe versions of the Thunder-380 are equipped with extended magazines, which hold nine rounds of 9mm/.380 ammunition. Front sight is integral to the slide, rear fixed sight is dovetailed to the slide. Latest production pistols also feature an integral key lock, located above the trigger, on the left side of the frame.
FN / Browning M.1900 (Browning No.1) pistol (Belgium)

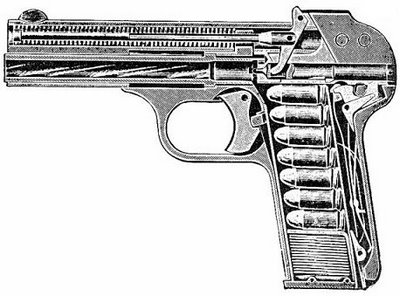

Type: Single Action, semi-automatic pistol
Chamber: 7.62x17mm SR (.32ACP)
Weight unloaded: 625 g
Length: 172 mm
Barrel length: 102 mm
Capacity: 7 rounds
The FN / Browning model 1900 pistol was a first of a long and extremely successful series of the Belgian-made pistols, designed by the American firearms genius John Moses Browning. The first semi-automatic, blowback operated pistol was designed by J. M. Browning circa 1896 and latter improved by the 1897. He offered his design to Belgian company FN Herstal circa 1898, and production began in 1899, as the Modele 1899. in 1900, this pistol, in slightly modified form (with barrel shortened from 122 to 102 mm), was adopted by Belgium as Mle.1900. Relatively simple and well designed, this pistol is also known as the Browning Number 1 pistol (Browning No.1). Widely used across Europe as a civilian and police sidearm, this was chambered for a new smokeless round, 7.62x17mm SR, which is also known in Americas as the .32ACP (.32 Colt Automatic). FN - Browning M1900 was widely copied in many countries, especially in S-E Asia. It was manufactured until the 1911 or so, with more than 700 000 pistols made.
Technical description.
The M1900 is a blowback operated, semi-automatic (self-loading) pistol. The barrel is fixed to the frame. The recoil spring is located within the slide and above the barrel. This spring, via special lever, also acts as a firing pin spring. M1900 is a striker fired, single action weapon. Unlike all latter designs, the ejection port is cut in the frame, and not in the slide. Safety switch is located at the left side, above the grip panel. Magazine is removable, is inserted into the pistol handle and holds 7 rounds. Magazine catch lever is located at the heel of the grip. Sights are fixed.
Browning 1910, 1922 and 380




Type: Single Action
Chamber: 7.65x17mm Browning (.32ACP) and 9x17mm Browning (.380ACP)
Weight unloaded: model 1910 - ca. 590 g; model 1922 - ca. 700 g
Length: model 1910 - 153 mm; model 1922 - 178 mm
Barrel length: model 1910 - 88 mm; model 1922 - 113 mm
Capacity: model 1910 - 7 (7.65mm) or 6 (9mm) rounds; model 1922 - 9 (7.65mm) or 8 (9mm) rounds
Model 1910 pistol had been developed by John M. Browning for Belgian company Fabrique Nationale (FN), Herstal. Model 1910 had been developed around two cartridges, also designed by Browning - the 7.65mm Browning, also known as .32ACP, which had been developed around 1900 for FN / Browning model 1900 pistol, and the 9mm Browning Short (9x17mm), also known as .380ACP, which, in turn, had been developed about 1908 for Colt / Browning model 1908 pistol.
In 1922, Browning modified the original pistol to suit requirements of the Jugoslavian military - he lenghtened barrel, enlarged the grip and magazine capacity by two rounds. The slide was lenghtened by adding removable frontal portion to the model 1910 slide.
Both models 1910 and 1922 were manufactured in large quantities until 1983 or so, when these guns were replaced by FN model 140DA / Browning BDA380 pistols. In the USA both model 1910 and model 1922 were imported under the name of "Browning 380 pistol", chambered in .380ACP. After the 1971, these guns have had ajustable target-type sights and slightly enlarged grips to suit new US gun laws. Between two World Wars these pistols became very popular across Europe as a police, military and self-defence guns. It is well-known also that the First World War was started by the Browning m1910 pistos, which had been used in 1914 to assasinate the Archduke Ferdinand.
Technically, both m 1910 and m 1922 (also known as model 1910/22), are blowback operated semi-automatic pistols. The recoil spring is located around the barrel, the trigger is of single action type and the gun is striker-fired. Both models featured three safeties - magazine safety (which blocks the firing when magazine is removed), automatic grip safety and manual, frame mounted safety.
Fabrique Nationale (FN) Browning "High Power"

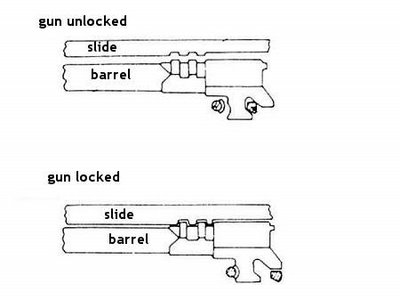




Type: Single Action
Chambering: 9mm Parabellum (also 7.65mm Parabellum and .40S&W in commercial/civilian models)
Length overall: 200 mm
Barrel length: 118 mmWeight: 885 g
Magazine: 13 rounds (10 rounds in .40SW)
Initially, the "High Power" pistol was designed by John M. Browning in 1925 and was patented in the USA in 1927, soon after the death of the Browning. The design was aquired by Belgian state-owned company FN Herstal, and improved by FN designer Dieudonne Saive. The resulting pistol was shelved until 1935, when Belgian army was ready to adopt new sidearm. The HP was offered for trials and won, and was adopted as a Model 1935 pistol. Soon after that it was also adopted by Belgian police and by many foreign countries, including Britich Commonwealth ones (UK, Canada, Australia etc.). The High Power is the only sidearm that served for both sides in WW2 - Germany used many HPs manufactured in occupied Belgium, while Allies used HPs manufactured mostly in Canada by company Inglis. The HP continues its service well into XXI century with belgian Army and Police, British army and many other military and Law Enforcement agencies, being second longest living service pistols after the another famous Brownings' design, the Colt 1911.
Thechnically, the High Power pistol, also known as Browning HP 35, GP 35 or Model 1935, is a recoil operated, locked breech pistol. It uses linkless barrel to slide locking (see picture above), invented by Browning. The trigger is single action, with external hammer. Original HPs featured frame mounted safety at the left side of the frame, that locks both sear and slide. Modern versions, since Mark II, also featured ambidextrous safety levers, that are also more comfortable to operate. Original HPs were available with two sight wersions - with standart fixed sights, and with rear tangent sights ajustable for distance from 50 to 500 meters. Some pre- and WW2-time guns also featured backstraps with cuts to accomodate removable shoulder stocks/holsters. Grip panels were made from wood, and pistols were availabli with or without lanyard rings. The HP was the first military pistol to have high capacity, staggered column magazine for 13 rounds plus one loaded in the chamber.
Newer Military/LE versions, such as Mk.II and recent Mk.III (also marketed under the name of HP-SA with added firing pin safety), featured more modern fixed combat sights and polymer grip panels. Commercial models may feature different sight options and finiches. Lates addition to the High Power family is a variation chambered in .40S&W cartridge. It has redesigned and strenghtened slide to accomodate more powerful cartridge, and magazine capacity of 10 rounds.
In 1980's or so FN also developed version of the HP with double action trigger, that was named HP-DA. It is still marketed by FN, but didn't catch the market as well as its predescessor did.
Copies and clones of the HP are still manufactured around the worls, such as Hungarian FEG 9, Bulgarian Arcus etc.
Browning BDA 380 (Belgium)


Type: Double Action
Chamber: 9x17mm (.380ACP) or 7.65x17mm (.32ACP)
Weight unloaded: 640 g
Length: 173 mm
Barrel length:
Capacity: 12 (9mm) or 13 (7.65mm) rounds
The Browning BDA 380 pistol was introduced in 1980 or so as a compact and lightweight pistol for police and civilian use. The gun was manufactured in Italy under contract from FN Herstal (Belgium) and marketed as FN model 140DA (in Europe) or Browning BDA 380 (in USA). Some sources said that BDA 380 is a copy of Beretta 84, but close inspection shows some differences (i.e. Beretta 84 has frame mounted safety while BDA 380 has slide mounted safety). The manufacture of the BDA 380 was ceased circa 1997. It was adopted by Belgian police.
The BDA 380 is a blowback operated, double action semi automatic pistol. It has aluminium alloy frame and steel slide. Ambidextrous slide mounted safety switch disconnects the trigger from the hammer when engaged. The pistol featured low profile fixed sightst and was available in either polished steel or blued finish, with wooden grip panels.
The gun deserved good reputation as reliable and comfortable to fire.
Browning DA / FN HP-DA / BDA9 / BDAO (Belgium)





Type: Double Action or Double Action Only
Chamber: 9x19mm Luger / Parabellum
Weight unloaded: 905 g (current model); 850 g (early model); 710 g (compact model)
Length: 200 mm standard model; 173 mm compact model
Barrel length: 118 mm standard model; 96 mm compact model Magazine
capacity: 14 rounds standard; also 7 rounds for compact models
Due to increased popularity of the military-style double action pistols, engineers of the Belgian FN Herstal company developed a double action variation of their famous FN / Browning "High Power" (GP35) pistol. First appeared in 1983, the new pistol was called as Browning Double Action (for American market) or FN HP-DA (for European market). Having similar construction and general outlines similar to old High Power pistol, the new gun differed from it in some ways. First of all, it has Double Action trigger with ambidextrous, frame mounted decocker lever instead of manual safety. Hammer spur was decreased in size, triggerguard reshaped for better two-hands hold. Slide also had slightly different contours of the front part. Magazine capacity was increased by 1 round and now it hold 14 rounds plus one in the chamber. Along with Standard version FN developed a Compact (HP-DAC) and Medium (HP-DAM) versions of the basic design. Compact pistol had shortened barrel, slide and grip, which held shortened, dual-stack magazine with 7 rounds. Standard, 14 rounds double-stack magazines also fit to Compact model. Medium model was a hybrid of the Standard frame and Compact barrel and slide. Due to some reasons, neither model sold well and FN discontinued this line circa 1987.
Later, in 1990, FN decided to bring a Double Action High Powers back to life. Using new manufacturing processes and a redesigned DA trigger, FN engineers produced a new variations, called Browning BDA9 and BDAO (for American market) or FN HP-DA and HP-DAO (for European market). BDA9/HP-DA differed from earlier HP-DA very little (most visible change is in decocking lever - newest guns has longer, triangle-shaped levers for better control). BDAO / HP-DAO is a further step down to modern trends and is a Double Action Only gun, withouth any manual safeties or decocker levers.
Unlike the original HP-DAs, newest models found its niche on European military and police market, and also sold in USA.
Technically, HP-DA / BDA9 is a recoil operated, locked breech semiautomatic pistol. It uses Browning cam to interlock barrel and slide. Trigger is of double action type with ambidextrous decoker and internal fireing pin safety or of double action only type with firing pin safety only. Additional safety prevents pistol from firing if slide does not closed completely. Basic design featured fixed sighst that are dovetailed into the slide. Magazine is double-stack and holds 14 rounds. Magazine release button is located behind the triggerguard and can be installed on either side of the gun by the user.
In general, the HP-DA / BDA9 pistol represents slightly conservative, but still sound approach to combat pistol, offering good firepower, reliability and reasonable safety level.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)